Writing header, configuring I/O pins, using delay function and switch operator
The only purpose
of this program is to turn on a few LED diodes on port B. Anyway, use this example to study what a real program looks
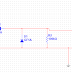
like. Figure below
shows connection schematic, while the program
is on the next page.
When switching on, every other LED diode on the port B emits light, which indicates that the microcontroller is properly connected and operates normally.
This example describes a correctly
written
header. It’s the same for all the programs
described in this book. To skip repetitiveness,
it will not be written in the following examples, but is considered to be at the beginning of every program and marked as ‘Header’.
To make this example more interesting, we will enable LEDs connected to the port B to blink. There are several ways to do it:
1. As soon as the microcontroller is turned on, all LEDs will emit light for a second.
The Delay function is in charge of it in the program.
It’s only needed to set delay expressed in milliseconds.
2. After one second,
the program enters the for loop
and remains there as long as the variable k is less than 20.
The variable is incremented by 1 after each iteration. Within the for loop, the switch operation
monitors
port B logic
state. If PORTB=0xFF,
its state is inverted into 0x00 and vice versa. Any change of these logic
states causes all LEDs to blink. Duty Cycle is 5:1 (500mS:100mS).
3. When the program exits the for loop, the port B logic state changes (0xb 01010101) and the program enters the endless whileloop and remains there as long as 1=1. The port B logic state is inverted each 200mS.














0 komentar: